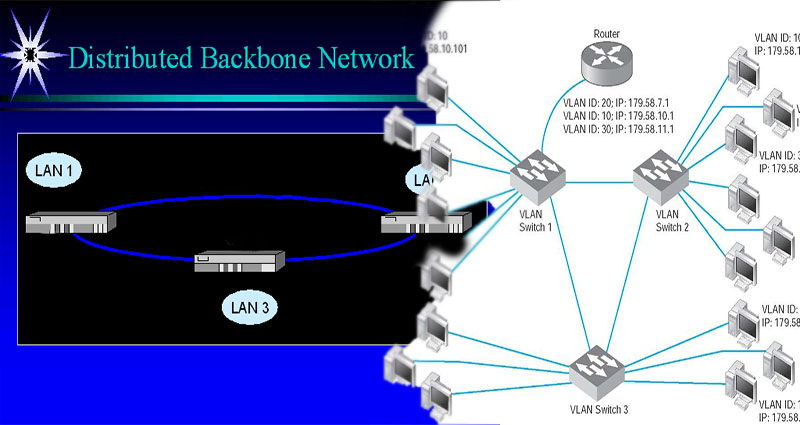
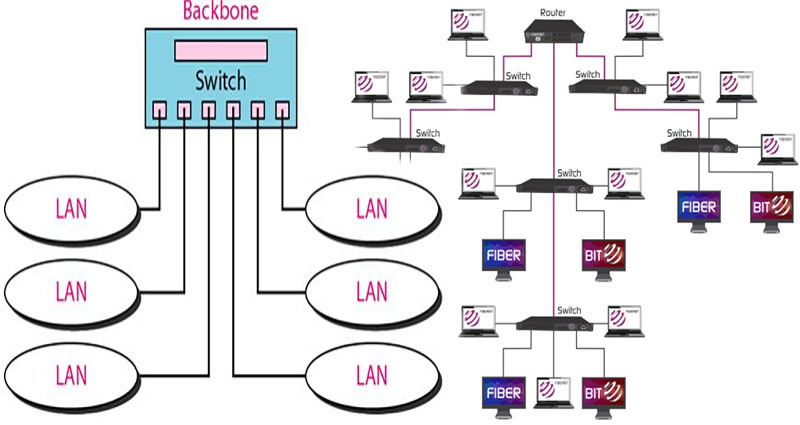
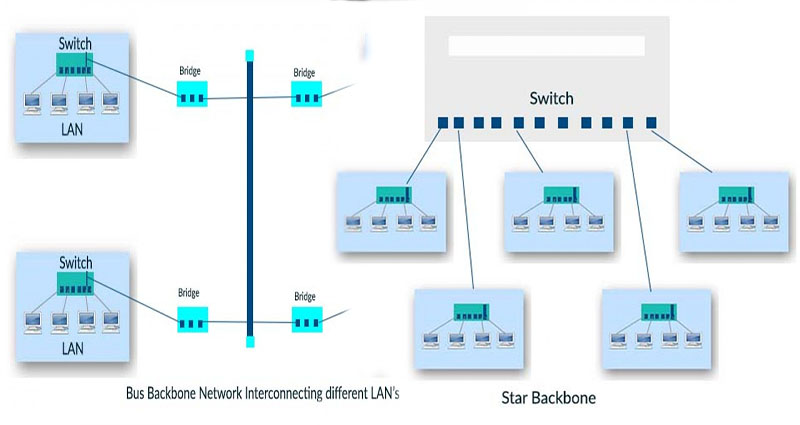
What Is a Distributed Backbone Network?
In a distributed backbone network, information is sent from a LAN terminal on the backbone to another LAN on the same bridge. Once information is sent to another LAN, the LAN connects to the backbone bridge, forms a frame of data, and sends it to the destination LAN and terminal through the backbone. Each backbone bridge maintains a table of LANs. Backbones may be Gigabit Ethernet or Fiber optic cabling.
Bus backbone structure
A distributed bus structure is used to connect multiple computers to form a network. It uses a backbone structure consisting of multiple switches, which are connected to each other. These switches act as the connection point between individual LANs. This structure has a limited scalability, and it only works if all devices are connected to a central connection point. In a distributed bus, however, each device is connected to a different set of switches, which form a … Continue reading >>>