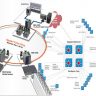
 Backbone network (bearer network) The underlying nodes of a multilevel distributed network, supplying communication solutions for the rest of the network (the hosts). As soon as the virtual circuit is ready, the LAN packet is broken into the series of ATM cells, and transmitted more than the ATM backbone employing the ATM virtual circuit identifier. Fiber Distributed Information Interface (FDDI) is a set of requirements initially designed in the late 1980s for use in MANs (ANSI X3T9.five), but has given that made its way into backbone networks. The most prevalent boundary exactly where firewalls are applied is in between an organization’s internal network and the net.
Backbone network (bearer network) The underlying nodes of a multilevel distributed network, supplying communication solutions for the rest of the network (the hosts). As soon as the virtual circuit is ready, the LAN packet is broken into the series of ATM cells, and transmitted more than the ATM backbone employing the ATM virtual circuit identifier. Fiber Distributed Information Interface (FDDI) is a set of requirements initially designed in the late 1980s for use in MANs (ANSI X3T9.five), but has given that made its way into backbone networks. The most prevalent boundary exactly where firewalls are applied is in between an organization’s internal network and the net.
Ahead of we talk about these architectures, we initially will have to discuss the way in which network designers think about backbone designs and how to combine them that is, the distinctive layers of backbones that exist in most organizations now. As the shared circuits in LANs and BNs have turn into overloaded with website traffic, networks are starting to use switched point-to-point circuits rather than shared multipoint circuits. On a large scale, a backbone is a set of pathways to which other big networks connect for lengthy distance communication.
Switched Backbones: most typical form of backbone, made use of in distribution layer, utilized in new buildings, occasionally in core layer, can be rack or chassis primarily based. Despite the fact that website traffic engineering calculations and circumventing congestion are prevalent in the phone network, common IP networks and their related routing protocols do not present this capability as readily. The FDDI-MAC scheme utilizes a variation of the IEEE 802.5 token-passing common used for token-ring networks with two varieties of tokens: absolutely free tokens and busy tokens.
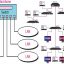
Every of these LANs and WLANs are connected into a switch for that floor, therefore forming a switched backbone on each and every floor. Both of these ATMs seem to be great options for desktop connections when ATM backbone networks are used. The technologies operate by offering a high speed circuit that is shared amongst all computers on the LAN or backbone network.
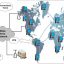
Backbone network development in these places may possibly call for some type of public assistance, either through economic support or by means of the provision of simpler access to current infrastructure. In Nigeria, at least 4 of the main operators are developing high-capacity fibre-optic cable networks capable of supporting high-bandwidth services, and a related pattern is emerging in Kenya. These networks are concentrating on important urban locations and on interurban hyperlinks where the majority of shoppers are.