Choosing the right type of topology for a local area network depends on its physical layout and connection methods. Here we will cover the various topologies of local area networks, their security measures, and some examples of local area networks. Ultimately, you should choose the type of network that best meets your needs. Listed below are some of the most common types of network topologies. Read on to find out which one would work best for you.
Connection methods used in a local area network
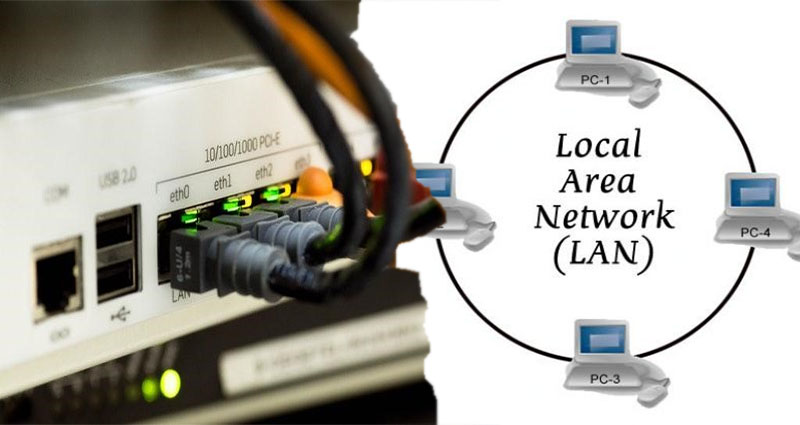
A Local Area Network, or LAN, is a group of connected computers in the same location. Each networked device can communicate with the rest of the network through Ethernet cables, Wi-Fi, or other media. In a LAN, only authorized devices may access the network. LANs were first used in the 1960s in colleges to catalog library collections, schedule classes, record student grades, and share equipment resources.
There are many differences between a LAN and a WAN. The first differs in the amount of bandwidth it can support, but is more reliable. A LAN connects two or more computers in a smaller geographic area, while a MAN connects multiple LANs. Both networks can be configured to connect multiple computers, though LANs are typically cheaper to setup and maintain. They also offer higher speeds.
Physical layout of a local area network
The physical layout of a local area network refers to the connections among the different hardware devices on the network. This topology is made up of switches, routers, and adapters on computers. These components are connected to each other via cables. In this design, the signal travels both ways to all the machines on the network, and then to its intended recipient. The data is accepted depending on the machine’s address.
The LAN is made up of various data equipment, such as a printer, database, or web server. These devices make up the LAN, and they communicate with one another through a common Transmission Medium. This transmission medium, which is usually a cable, provides the necessary transmit and receive capability and all the intelligence needed to send and receive information. It is important to understand how the physical layout of a LAN affects its performance.
Security measures
One of the most important aspects of a LAN is security. Security measures for the LAN should include internal measures that prevent viruses from entering the network via email or downloading from a rogue source. Anti-virus and malware security is necessary to combat hacking activities that originate internally. This article will discuss the basics of LAN security and how it can be implemented. It will also discuss some of the common methods of local network security.
MAC address filtering prevents intruders from gaining access to the network. This security measure involves collecting MAC addresses from network devices and uploading them to the router’s database. It ensures network security by preventing hackers from accessing the network without the MAC address. This is also a good method to protect Wi-Fi networks. However, it may not be appropriate for every organization. For instance, a Wi-Fi network should be secured by MAC address filtering to prevent hackers from connecting to it.
Examples of a local area network
A local area network (LAN) is a system that connects computers and other devices in a specific location. These networks can be large or small, but usually remain within a single building. LANs allow for easy sharing of files, printers, and other resources. Examples of LANs include office buildings and nuclear power plants. They also provide a consolidated interface for data storage on multiple physical devices. Many devices have embedded computer systems, which create a local area network to extend functionality.
These networks are governed by hardware, such as routers and switches. The routers ensure that data packets reach their destination. Hubs, on the other hand, allow participants to connect to each other. In today’s LANs, hubs are rarely used. This is because of their complexity. In today’s networks, switches and routers are the primary components of local area networks.
Listed below are common hardware components and examples of a local area network.