Switched Backbone Networks
Switched backbone networks can support very high traffic volumes, but the performance can be limited by poor interconnectivity. In addition to the complexity of backbone devices, some newer technologies still lack fully developed standards. In this article, we’ll look at Star topology, Layer 2 switches, Gigabit Ethernet, and ATM-25. To learn more, read our articles on Ethernet and ATM. This will help you decide which backbone technology is right for your business.
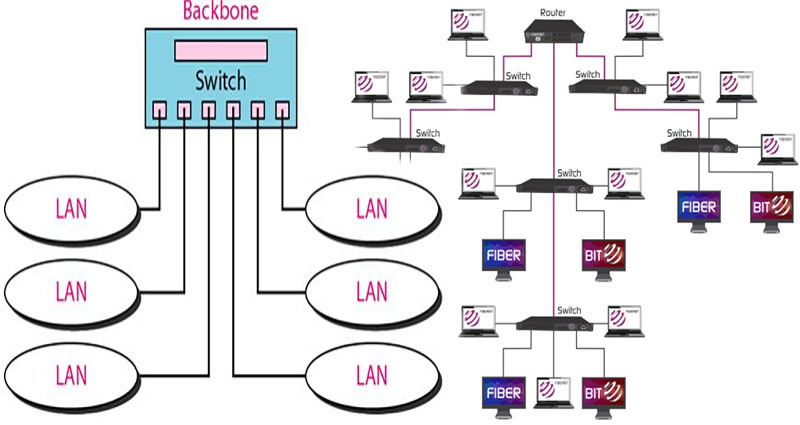
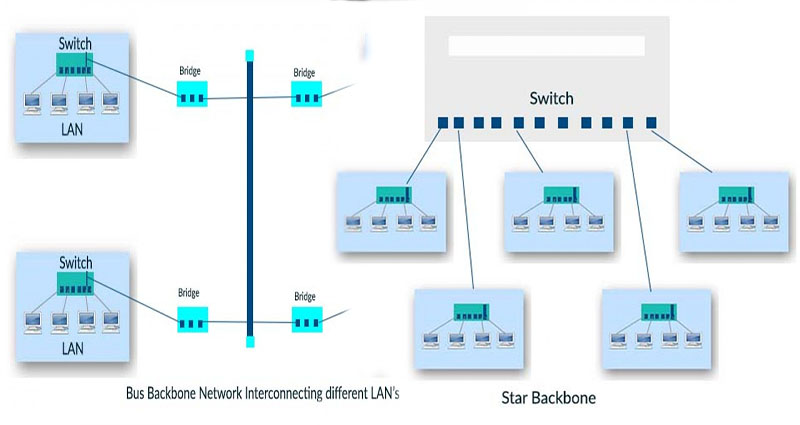
Star topology
A star topology in a switched backbone network allows multiple sites to communicate with each other through one central site. The central site is called a core switch. The second switch is connected to the core switch through chassis stacking technology, which assigns computers to segments using software and hardware. Each segment has a special subnet address that can be managed by a different network manager. The star topology is used in both wired and wireless … Continue reading >>>