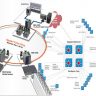
Is a generally applied application that uses a net browser and flash to test the connection speed from a device to a selected point on the World wide web. In the above image, accomplished by Donna Cox and Robert Patterson of the NCSA, is a visual representation of what an Internet backbone in the United States. Most organizations now use switched backbones in which all network devices for a single element of the building are physically positioned in the similar space, typically in a rack of equipment. Routers connect two or much more LANs that use the same or distinct information link protocols, but the same network protocol. The purpose of the backbone is to connect regional distribution networks and, in some instances, to offer connectivity to other peer networks.
Is a generally applied application that uses a net browser and flash to test the connection speed from a device to a selected point on the World wide web. In the above image, accomplished by Donna Cox and Robert Patterson of the NCSA, is a visual representation of what an Internet backbone in the United States. Most organizations now use switched backbones in which all network devices for a single element of the building are physically positioned in the similar space, typically in a rack of equipment. Routers connect two or much more LANs that use the same or distinct information link protocols, but the same network protocol. The purpose of the backbone is to connect regional distribution networks and, in some instances, to offer connectivity to other peer networks.
If a network backbone goes down your Web connection speed can be drastically decreased or might not even be able to get to specific locations in the globe. The Internet has no centralized governance in either technological implementation or policies for access and usage each constituent network sets its own standards. Moreover, PVC sizing demands that the targeted traffic levels amongst any two distribution networks ought to be well understood, or that the network has the capability to circumvent congestion. Higher-bandwidth backbone networks are a key portion of the investment necessary for broadband in Africa.
As soon as the virtual circuit address for the destination information link layer address has been discovered, it can be applied to transmit the packet through the ATM backbone. Distributed procedures are normally used to control the operation of the backbone network in order to decrease the possibility that a single failure could disrupt the entire network. As the one can see from Figure 1, serial backbone can be made not only from switches, but also from gateways and routers.
This kind of switched backbone is shown graphically in Figure 8.7. This has the advantage of putting all network gear in one place for easy upkeep and upgrade, but it does demand a lot more cable. Most backbone topologies are, as a result, initially developed based on economic constraints, such as user population density, or application needs and WAN service availability.
Several networking technologies work collectively as connection points or nodes, and are connected by distinct mediums for transporting data like optical fiber, classic copper and even wireless technology like microwave and satellites. Serial backbone is formed of two or extra devices that are connected in a daisy chain (linked series). ATM backbone switches commonly deliver point-to-point complete duplex circuits at 155 Mbps (total of 310 Mbps).