There are several different types of surveillance methods available. We’ll go over Active surveillance, Passive surveillance, Integrated surveillance, and biometric surveillance. Each has their own set of benefits and drawbacks. The purpose of this article is to give an overview of these different forms of surveillance, and how each can be used in public health. Once you’ve read this article, you’ll know how to choose the best surveillance method for your needs.
Active surveillance
Active surveillance is an ongoing process aimed at identifying and preventing disease outbreaks. These methods use various sources of data, such as emergency rooms, hospital and medical records, and immunization and lead poising prevention programs. They may also involve environmental data and pharmacy medication sales. The process begins with the definition of a case, which may involve fewer signs or expanded suspicions about a common cause. The next step is to collect relevant screening laboratory data.
Passive surveillance
There are several different types of surveillance, including active and passive. Both types are vital for assessing disease trends and risk factors, and they require expert attention and systemic evaluation. The future of surveillance will rely on communication to improve data collection, analysis, and dissemination. In addition, the methods and technologies for surveillance are evolving, and there are several issues to consider when implementing a surveillance system. This article will discuss some of the challenges and potential benefits of passive surveillance.
Integrated surveillance
Integrated surveillance is a trend that has been growing for several years. Integrated surveillance systems provide a holistic view of disparate data and enable enhanced risk mitigation and business insights. However, many smaller firms have yet to invest in such programmes despite the benefits. Agility requires easy access to information, and scattered data makes it difficult to react quickly to threats, market movements, and regulatory changes. This trend is expected to continue, as data management capabilities become increasingly important.
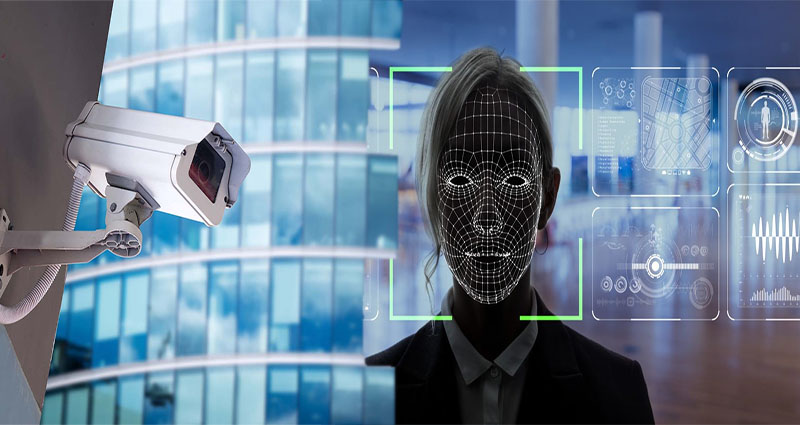
Biometric surveillance
While there is no privacy law governing biometric data, some states and police agencies have taken the lead to make the data more private. In fact, one state has passed a law to limit the use of biometric data by law enforcement. ICE recently requested driver’s license information from Illinois, which rejected the request. The ECtHR has upheld this principle. If law enforcement wants to use biometric data for multiple purposes, there is a need to protect personal information.
PTZ surveillance cameras
There are different kinds of surveillance cameras, and each has its own advantages and disadvantages. PTZ surveillance cameras are often the most effective option for open areas such as parking lots, warehouses, and docks, where the wide view provides better coverage. A PTZ camera can only monitor one location at a time, so installing three or four standard cameras may be sufficient. High-performance PTZ cameras can increase the effectiveness of your surveillance system as well.
FETPs
Graduates from FETPs are typically involved in managing public health surveillance systems, conducting research and analysis, and training public health workers. Other common activities are investigation and response to outbreaks, and the use of computers for specific applications. The least common activities involve writing scientific research articles. This study addresses both needs. In addition, the results are encouraging. However, more studies are needed to gauge the impact of FETPs and other surveillance programs.
Covert listening devices
Surveillance technologies are increasingly being used to monitor people’s activities. These devices can be installed anywhere to record conversations and provide crucial evidence. In many cases, covert listening GPS devices are more helpful than video surveillance, since audio provides crucial clues and context for visuals. The ability to record conversations and listen to audio makes them useful for a variety of purposes, from monitoring children to gathering evidence of infidelity.