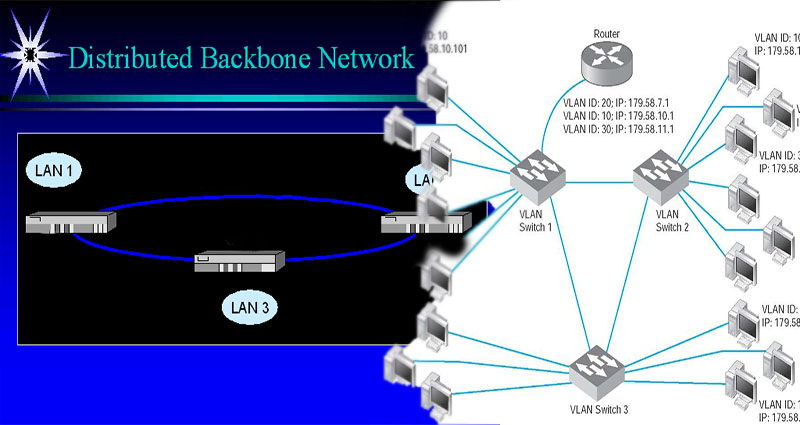
In a distributed backbone network, information is sent from a LAN terminal on the backbone to another LAN on the same bridge. Once information is sent to another LAN, the LAN connects to the backbone bridge, forms a frame of data, and sends it to the destination LAN and terminal through the backbone. Each backbone bridge maintains a table of LANs. Backbones may be Gigabit Ethernet or Fiber optic cabling.
Bus backbone structure
A distributed bus structure is used to connect multiple computers to form a network. It uses a backbone structure consisting of multiple switches, which are connected to each other. These switches act as the connection point between individual LANs. This structure has a limited scalability, and it only works if all devices are connected to a central connection point. In a distributed bus, however, each device is connected to a different set of switches, which form a network.
Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet is a high-speed, high-capacity networking standard for enterprise networks. Its Ethernet framing standard, 802.3, supports up to 1 Gbps of bandwidth and uses a technology known as Carrier Sense Multiple Access (CSMA/CD) to detect and handle collisions between transmissions. This protocol is used for many purposes in enterprise networks, including connecting servers, workstations, and routers for high-bandwidth applications.
Fiber optic cabling
The distributed backbone network uses fiber optic cables as its communications infrastructure. Fiber optics are a popular choice for building backbone networks and have revolutionized the telecommunications industry. They work in environments with electromagnetic interference and offer more power and flexibility than copper cabling. Smart building platforms can help users get the most out of fiber optic cabling and maximize its potential. Listed below are some important things to consider when installing fiber optic cabling.
Star backbone structure
A distributed backbone network has multiple components. It connects each LAN with a backbone that acts as a superhighway, or “backbone,” connecting the different networks. The capacity of the backbone is expected to exceed the number of supported networks. The star backbone structure consists of wiring hubs that serve as connections between the LANs. This is also known as a hybrid backbone network, which combines a distributed backbone with hubs.
Point to point network
A computer network’s backbone is either a single box or a series of interconnected units. The type of backbone you use will depend on the demands of your business. The infrastructure you choose should provide ample bandwidth to all of your users, and be able to be stretched as needed. A backbone that is designed properly can also support multiple logical functions. It can also serve as a backbone for a large enterprise.
Internet as a backbone
The Internet is an extremely vast network and is commonly referred to as a backbone. It is comprised of many networks and is often divided into multiple types, depending on the traffic they carry. Some of the largest backbone networks are made up of large computer networks connected to other high-capacity networks. These networks often contain network centers that exchange traffic between continents and countries. These backbone networks may also be classified as “core routers” of the Internet.